Field Equipment
Field vane shear
The geotechnical field vane shear test is an in-situ test that determines the undrained shear strength of soft, saturated clays by rotating a four-bladed vane pushed into the ground and measuring the torque required to shear a cylindrical section of soil.
The field vane shear testing device has the following features:
- Digital torque wrench with output to computer
- Rotation applied manually
- Deployed up to 10m depth with custom drill rod
- Variety of vane shapes and H/D options
Dynamic penetration testing
In-borehole dynamic penetration testing
- Well-suited for in-situ characterization of coarse grained soils such as gravelly soils, rockfills, tailings and waste materials
- Operated in a similar manner as SPT
Dual-mass dynamic cone penetration testing (DCP)
- Manual and portable
- For shallow (<5’) penetration resistance assessments
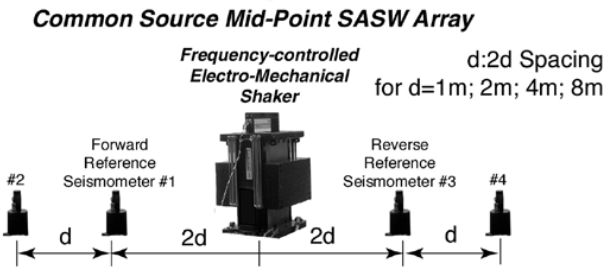
Multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) and microtremor analysis method (MAM) equipment
MASW and MAM equipment are used in geotechnical engineering to assess subsurface stiffness by analyzing the propagation of surface waves. MASW utilizes actively generated seismic waves, while MAM uses passive ambient vibrations, both providing valuable shear wave velocity profiles for site characterization and seismic analysis.
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction (EMI) is a non-invasive geophysical method that measures the subsurface's electrical conductivity by inducing and detecting electromagnetic fields. This helps characterize soil and rock properties, map geological layers, identify groundwater variations, and detect buried objects or contamination.
The testing system consists of:
- Geophex GEM2 Frequency domain electromagnetic induction (FDEM) device. 1.66m fixed length with simultaneous transmission of up to 10 frequencies from 30 Hz to 96 kHz.
- Trimble Nomad 900 or Microsoft surface data logger.
Uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs) and sensors
UAVs are used in geotechnical engineering to capture high-resolution aerial imagery and create 3D models of sites, enabling detailed mapping, inspection, and monitoring of ground conditions, slopes, and infrastructure, particularly in difficult or hazardous areas. This technology enhances site characterization, aids in identifying potential instabilities, and assists in progress tracking and post-disaster assessment.
GreenValley LiAir V70 LiDAR
An integrated sensor unit consists of a Livox Avia LiDAR and a Sony A5100 visible-light camera. The LiDAR is operating at the 905 nm wavelength (near-infrared range) with a field of view of 70.4° (horizontal) by 4.5° (vertical).
DJI Zenmuse XT2 Thermal Camera
An integrated unit consists of a FLIR thermal infrared camera and a visible-light camera. The thermal camera operates at the spectral band of 8 – 14 μm.
MicaSense RedEdge-MX Multispectral Camera
An imaging sensor that can capture images in five distinct spectral bands, centering at 475 nm (blue), 560 nm (green), 668 nm (red), 717 nm (red edge), and 840 nm (near infrared).
Terrestrial robots - Boston Dynamics SPOT
Boston Dynamics Spot is an agile, four-legged robot capable of navigating diverse and challenging terrains at speeds up to 1.6 m/s with an average runtime of 90 minutes. It is designed for tasks like inspection and data acquisition, supporting a payload capacity of up to 14 kg.
Real-time kinematic GPS
Available models include Emlid GNSS receivers, which is designed for surveying, RTK, PPK, and general GNSS applications with NTRIP compatibility. These versatile units offer continuous data collection for robust PPK corrections or integrated workflows for easy point collection and stakeout. Benefit from simultaneous connectivity to multiple satellite constellations (GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS, Galileo, QZSS, SBAS) for reliable performance. Our inventory also includes a range of models, from single-frequency RS units to advanced multi-frequency RS2/RS2+ units and the compact Reach M2 module for UAVs.
Terrestrial Lidar scanner – Trimble X9 terrestrial scanner
The Trimble X9 is a versatile terrestrial 3D laser scanner used to rapidly capture high-accuracy, detailed point clouds of environments, featuring capabilities like scanning up to 1 million points per second with a range typically up to 150 meters and millimetric accuracy for various surveying, construction, and engineering applications. It is designed for efficient reality capture and creating precise 3D models.
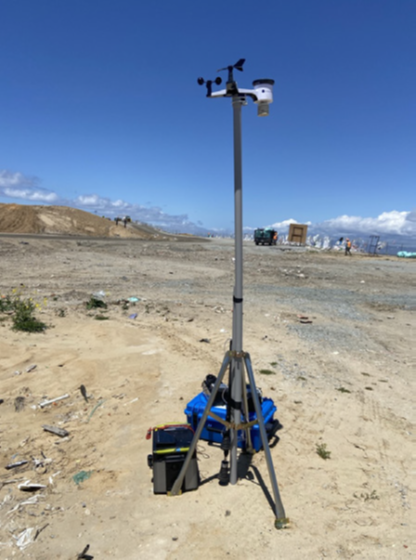
Portable weather station
This portable weather station provides real-time measurement of key atmospheric conditions including wind speed and direction, solar/UV light, precipitation, and barometric pressure. It can wirelessly download this data to an IoT server, enabling continuous monitoring and analysis of environmental data.
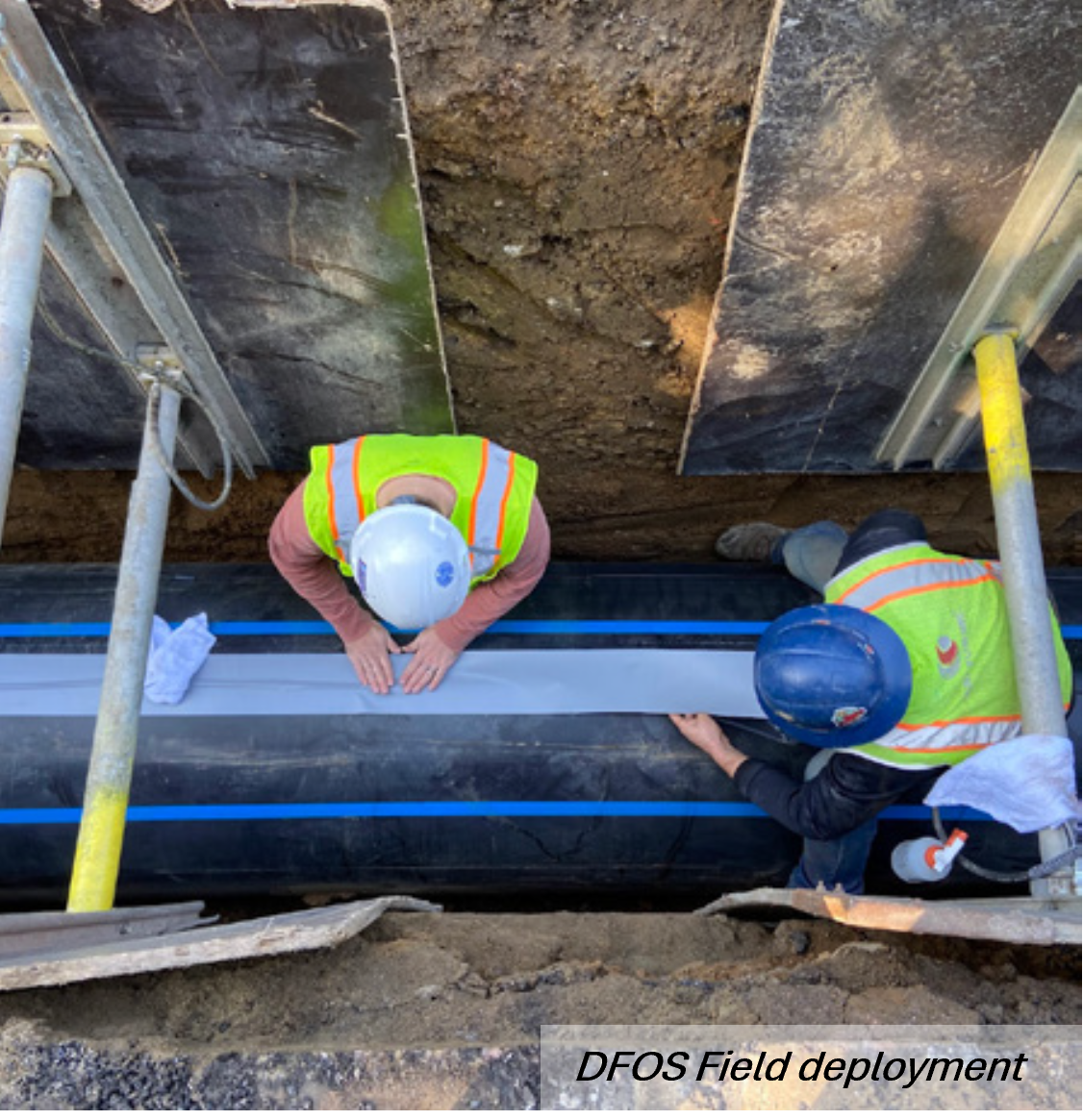
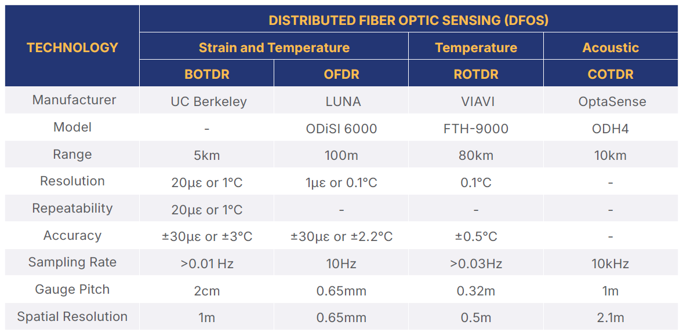
Distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS)
Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) is at the forefront of infrastructure performance monitoring of strain, temperature, vibrations, and sound along fiber optic cables over long distances at a high spatial and temporal resolution. Typical techniques include Distributed Strain Sensing (DSS), Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS), and Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS).

Tunable diode laser (TDL) sensor
TDL sensors detect methane by measuring how a laser tuned to specific wavelengths is absorbed by methane molecules, allowing for precise and selective concentration measurement.
Inspectra TDL sensor
- Measurement range: 0 – 10,000 ppm
- Resolution: 1 ppm
- Data frequency: 1 Hz
- Communication via an external Bluetooth device