Soil and Rock Mechanics Testing Laboratories
Consolidation Testing
Consolidation test measures the magnitude and rate at which a soil sample decreases in volume when subjected to a sustained static load, primarily due to the expulsion of pore water. It is crucial for predicting settlement of structures built on fine-grained soils.
| Device | Constant rate of strain | Incremental loading |
|---|---|---|
| Specimen diameter (in) | 2.5 to 4 | 2.5 to 6 |
| Pressure range | 1 kPa to over 10 MPa | 5 kPa to over 700 kPa |
| Additional features | Back pressure available |
Laboratory vane shear testing
Vane Shear tests provide a direct assessment of undrained shear strength of cohesive soil deposits either in the field, or on high-quality samples within their tubes in the laboratory. Unique features include
- Instrumented beam load cell for torque measurement
- Continuous torque recording through peak & residual
- Adjustable, steady rotation rate using electric motor
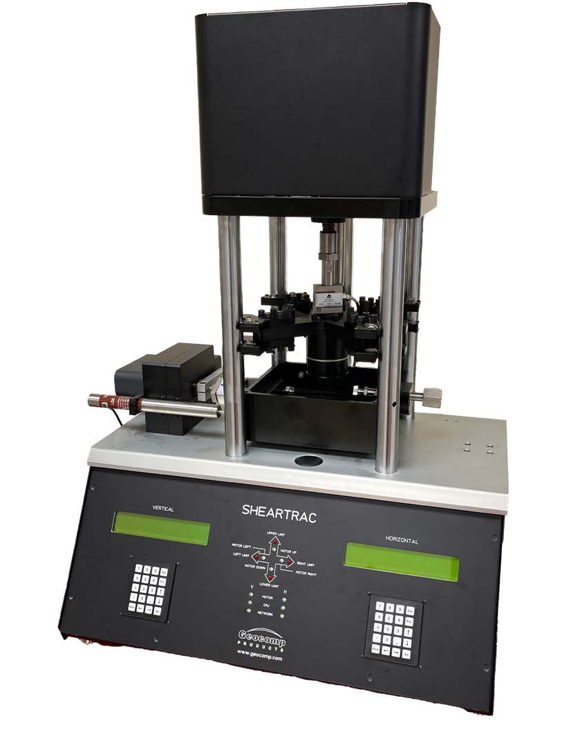
Simple shear testing
Simple shear testing subjects a soil specimen to shear stresses under controlled normal stress or volume conditions. Static simple shear determines the shear strength and deformation under steady loading, while dynamic simple shear evaluates the soil's response, such as stiffness and liquefaction potential, under cyclic loading conditions simulating earthquakes or traffic.
| Device | Geocomp cyclic DSS | CKC unidirectional simple shear | Bi-directional simple shear | Geocomp large diameter DSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen diameter (in) | 2.5 and 4 | Up to 4 | Up to 4 | 12 |
| Max vertical stress (kPa) | 3000 (d = 2.5’’) and 1000 (d = 4’’) | 700 | 700 | 550 |
| Cyclic loading frequency (Hz) | 0.033 to 1 | 0.01 to 1 | 0.01 to 1 | 0.01 to 1 |
| Additional features | Specimen can be submerged under water |
Equipped with chamber and back pressure for saturation and lateral stress control |
Equipped with chamber and back pressure for saturation and lateral stress control |
Modifiable to a Monotonic or Cyclic Interface Direct Shear |
| Other measurements | Vs | |||
| More Information | Link |
Triaxial shear testing
Triaxial test subjects a cylindrical soil sample to confining pressure and then applies axial stress to induce shear failure. Static triaxial tests determine shear strength parameters under drained or undrained conditions, while dynamic triaxial tests assess the soil's cyclic strength, stiffness, and pore pressure generation under repeated loading.
| Device | CKC electropneumatic automated triaxial test system | Large-scale triaxial test system |
|---|---|---|
| Specimen diameters (in) | 1.4, 2.8, and 4.0 | 12 |
| Consolidation | Isotropic and anisotropic | Isotropic |
| Max consolidation stress (kPa) | 500 | 700 |
| Loading | Monotonic and cyclic (frequency up to 1 Hz) | Monotonic and cyclic (frequency up to 0.1 Hz) |
| Additional features | Adapted for small strain levels with modular stress and strain instrumentation; Vs measurements available. |
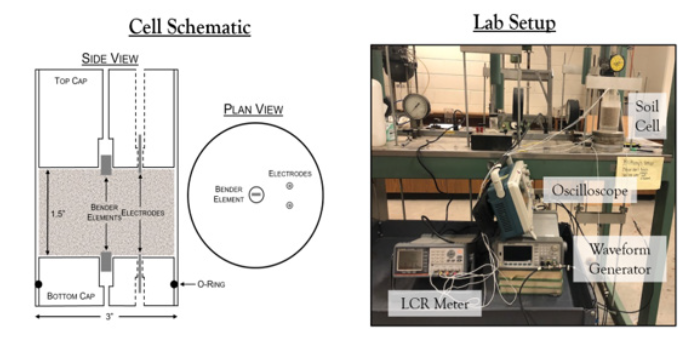
Soil electrical resistivity and Vs measurement
These geophysical methods are often used together to characterize subsurface soil conditions. Electrical resistivity measures the ground's opposition to electrical current flow, providing information about soil type, water content, and contaminants, while shear wave velocity measures the speed at which shear waves travel through the soil, indicating its stiffness and important for seismic site response analysis and liquefaction assessment.
Unique features include:
- Custom electrical resistivity apparatus using a Precision GW INSTEK LCR-6300 LCR Meter that can operate at 10 Hz to 300 kHz.
- Testing setup combined with bender element testing for shear wave velocity testing.
Table saw and rock coring
A table is used to cut rock samples into precise shapes and dimensions. A rocking coring device is utilized to obtain cylindrical rock cores of specific diameters by rotating a core barrel while applying pressure and a rocking motion to facilitate penetration and reduce binding.
Point load testing
The point load test is a simple index test used to estimate the rock's strength by applying a concentrated load through conical platens to a rock sample until failure. The test provides a point load strength index, which can be correlated to the unconfined compressive strength of the rock.
- Load frame with 55 kN capacity via mounted hydraulic ram and digital display showing load
- Rock core diameters up to 4 inches.
Ultrasonic velocity testing
Ultrasonic velocity testing is a non-destructive method that measures the speed at which ultrasonic waves (P-waves and S-waves) travel through a rock sample. This velocity provides insight into the rock's dynamic elastic properties, density, and the presence of fractures or other discontinuities.
This apparatus consists of:
- Agilent 33500B Series Waveform Generator
- Tektronix MSO 2012 Mixed Signal Oscilloscope
- Various direct contact transducers
- Vp Compressional - 150 kHz - 28mm diameter – Proceq
- Vs Shear - 250 kHz - 25mm diameter – Olympus
- Vs Shear - 1 MHz - 13mm diameter - Olympus
Electrical resistivity testing
Electrical resistivity testing for rocks measures how strongly a rock sample opposes the flow of electric current. This property is influenced by factors like mineral composition, porosity, water content, and the salinity of pore fluids, providing insights into the rock's internal structure and fluid saturation.
This apparatus uses
- Precision GW INSTEK LCR-6300 LCR Meter (operating frequency 10 Hz to 300 kHz).